As organizations accelerate their digital transformation journey, moving to the cloud has become a strategic imperative. However, managing cloud environments at scale can be challenging, especially when it comes to setting up a secure, scalable, and compliant infrastructure. This is where Azure Landing Zones and Accelerators come in—providing a structured approach to cloud adoption and deployment.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the concept of Azure Landing Zones, discuss their key benefits, and take a deep dive into the Azure Landing Zone Accelerators that streamline cloud adoption, ensuring a smooth transition to a robust, scalable cloud environment.
The following OV-1 based Conceptual architecture from Microsoft helps will help visualizes the typical resources / services that can deployed with the Microsoft Azure landing zone.
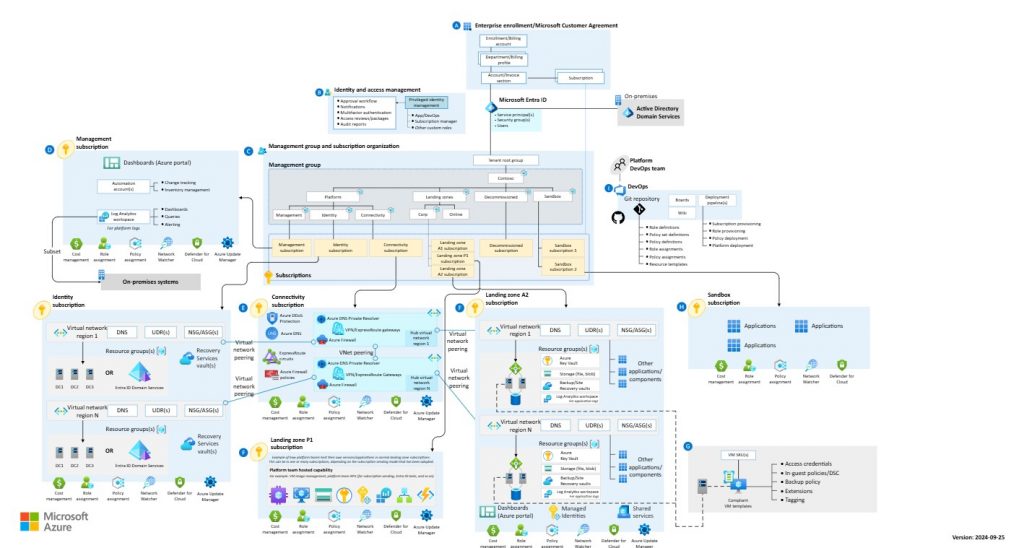
What is an Azure Landing Zone?
An Azure Landing Zone is a set of guidelines, best practices, and resources that help organizations set up an Azure environment that is ready for production workloads. It provides a scalable foundation aligned with Microsoft’s Cloud Adoption Framework (CAF), enabling organizations to deploy workloads with confidence.
The concept of landing zones is centered around establishing best-practice architecture, ensuring that cloud resources are organized, secured, and managed effectively. These zones are designed to support different workloads and scenarios, including hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Key Features of Azure Landing Zones:
- Scalability: Built to handle growth and evolving workloads without re-architecting.
- Security & Compliance: Aligns with industry best practices and regulatory requirements.
- Governance & Management: Ensures consistent management and governance using built-in policies.
- Cost Management: Optimizes resource usage to control cloud spending.
Why Azure Landing Zones Matter
When migrating to the cloud, it’s crucial to establish a well-architected environment that supports growth, scalability, and operational efficiency. Azure Landing Zones provide organizations with a structured approach to achieve this by:
- Standardizing Deployments:
- Consistent environments reduce deployment errors, improve efficiency, and ensure that resources adhere to organizational standards.
- Accelerating Cloud Adoption:
- Pre-configured templates and best practices help organizations rapidly set up Azure environments, reducing time-to-market.
- Enhancing Security and Compliance:
- Integrated security policies and compliance frameworks ensure that your Azure environment meets industry regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001.
- Optimizing Costs:
- Built-in cost management features help organizations control spending by optimizing resource allocation and usage.
Core Components of Azure Landing Zones
To create a robust Azure environment, landing zones focus on several foundational elements:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM):
- Leveraging Azure Active Directory (Entra ID) to manage user identities, roles, and access controls.
- Implementing policies like multi-factor authentication (MFA) to enhance security.
- Networking:
- Setting up Virtual Networks (VNets), subnets, and Azure Firewall for network segmentation.
- Configuring ExpressRoute or VPN Gateway for hybrid connectivity.
- Security and Compliance:
- Applying security policies using Azure Policy and Microsoft Defender for Cloud to protect resources.
- Ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements through Azure Security Center.
- Governance and Resource Organization:
- Using Management Groups, Azure Blueprints, and Tags for resource organization.
- Enforcing governance policies for consistent resource management across environments.
- Monitoring and Operations:
- Leveraging Azure Monitor and Log Analytics to track performance and detect issues.
- Automating responses to incidents using Azure Automation and Logic Apps.
Understanding Azure Landing Zone Accelerators
Azure Landing Zone Accelerators are a set of pre-built, automated tools and templates designed to simplify the deployment of landing zones. They are aligned with Microsoft’s Cloud Adoption Framework and are tailored to specific customer scenarios, allowing organizations to quickly establish a production-ready Azure environment.
Key Benefits of Azure Landing Zone Accelerators:
- Speed and Efficiency: Accelerators help reduce deployment time by providing ready-made templates that follow best practices.
- Scalability: Pre-configured solutions that can scale based on your organization’s needs.
- Customizability: The accelerators are modular, allowing you to customize them to fit your organization’s specific requirements.
Types of Azure Landing Zone Accelerators:
- Enterprise-Scale Landing Zones: Focused on large organizations with complex requirements.
- SAP on Azure Landing Zones: Optimized for deploying SAP workloads on Azure.
- AI and Data Landing Zones: Tailored for data-driven applications, analytics, and AI workloads.
- Healthcare and Finance Landing Zones: Designed to meet specific industry compliance and regulatory standards.
How to Deploy an Azure Landing Zone Using Accelerators
Deploying an Azure Landing Zone using Accelerators can be done through Azure Portal, Azure CLI, or Infrastructure as Code (IaC) using tools like Terraform and Bicep. Here’s a high-level overview of the deployment process:
- Assess Your Current Environment:
- Review your organization’s cloud readiness and define your specific requirements.
- Identify key workloads, compliance requirements, and performance needs.
- Select the Appropriate Landing Zone Accelerator:
- Choose an accelerator that aligns with your organization’s goals (e.g., Enterprise-Scale, SAP, AI/ML).
- Deploy the Accelerator:
- Use Azure Blueprints or ARM templates to automate the deployment of your chosen landing zone.
- Customize configurations as needed to align with your organization’s policies and standards.
- Configure Governance and Security Policies:
- Set up role-based access controls (RBAC), security policies, and compliance rules.
- Implement logging, monitoring, and cost management features.
- Test and Validate:
- Conduct a thorough review of the deployed environment to ensure it meets your requirements.
- Perform security and compliance audits before moving workloads to production.
Best Practices for Implementing Azure Landing Zones
- Start with a Clear Strategy:
- Define your cloud adoption strategy, focusing on business goals and outcomes.
- Use the Microsoft Cloud Adoption Framework to guide your planning and implementation.
- Embrace Automation:
- Use Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools like Terraform and Bicep to automate deployments.
- Leverage Azure DevOps pipelines for continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD).
- Implement Strong Governance:
- Use Azure Policy and Blueprints to enforce standards across your environment.
- Regularly review and update policies to align with changing business needs.
- Prioritize Security:
- Implement Zero Trust Architecture principles by securing identities, networks, and data.
- Continuously monitor your environment using tools like Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
- Optimize Costs:
- Use Azure Cost Management and Budgeting to monitor cloud spending.
- Leverage Azure Advisor recommendations to optimize resource usage and reduce costs.
Conclusion: Accelerate Your Cloud Adoption with Azure Landing Zones
Azure Landing Zones and Accelerators provide organizations with a powerful toolkit for rapidly deploying secure, scalable, and compliant cloud environments. By leveraging these solutions, organizations can streamline their cloud adoption journey, ensuring that their Azure environment is well-architected and optimized for growth.
Whether you’re just starting your cloud journey or looking to optimize your existing Azure environment, Azure Landing Zones offer a structured and efficient approach to achieving your cloud goals.